Gothic architecture emerged during the Middle Ages and began in Northern France and then spread to the rest of Western Europe. We often associate the term Gothic with darkness but in fact Gothic style was made to bring sunshine into people’s lives.

There were three phases of Gothic architecture, Early, High and Late Gothic. High Gothic was more elaborate and Late Gothic was even more so and sometimes referred to as ‘flamboyant architecture’. Previously, architecture has been much simpler in nature. The first phase, early Gothic, began near Paris and lasted from 1120-1200. The abbey of Saint Denis was the first surviving gothic structure and was built in 1140. Soon after the Notre Dame was built in 1163 and the gothic style spread throughout the rest of Western Europe. High Gothic was more elaborate and Late Gothic was even more so and sometimes referred to as ‘flamboyant architecture’.
Some key features of the Gothic style are pointed arches and stained glass windows. These arches are also a characteristic of Romanesque architecture, which the Gothic evolved from. Because cathedrals were built using heavy stone, traditional arched barrel vaults would collapse under pressure. The solution was to build thick vertical supporting walls to contain the barrel vault. Masons also chose pointed arches as oppose to domes and invented ribbed vaults which would add additional support to the ceiling. The weight of the roof was now channelled through the ribs of the ceiling and across the walls to a flying buttress which which was basically a semi arch and then down the the piers to the ground. The roof didn’t depend on the walls for support. This is why walls could be built very high and they would be thinner to give more room for the interior. Furthermore tracery, (the series of structural support between sections of glass) supported the weight of the wall while still leaving plenty of room for windows which were made of stained glass.
Stained glass windows depicted scenes from the bible in bright colours and stories were told using large panels, almost like a graphic novel. Using visual forms of communicating ideas were very effective as they spoke to the entire population and could be understood by those who were illiterate.

Stained glass was made up of a mix of sand and potash under high temperatures. The result was remarkable; colourful, translucent glass allowed light to pass through and brightened the interior of the cathedrals.
The abbey of Saint Denis is considered an architectural landmark for being the first example of Gothic style. Before the term Gothic emerged, it was known as the ‘French Style’. This structure served as a prototype for future cathedrals in France and later the rest of Europe.
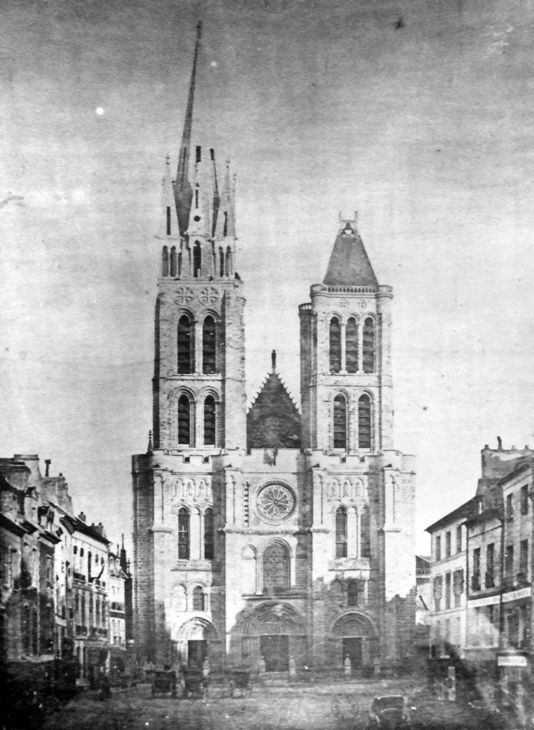
I’m a designer this week and was inspired by Gothic style particularly stained glass windows. I really like the contrast between glowing light and bright colours against darkness and want to convey this in my panel. I think it would be cool to tell a story similarly to what masons did when constructing cathedrals.
Citations:
“Gothic Architecture (C.1120-1500).” Gothic Architecture: Characteristics, History, http://www.visual-arts-cork.com/history-of-art/gothic-architecture.htm.
Boundless. “Boundless Art History.” Lumen, https://courses.lumenlearning.com/boundless-arthistory/chapter/gothic-architecture/.
“Stained Glass Windows in Gothic Architecture.” Study.com, Study.com, https://study.com/academy/lesson/stained-glass-windows-in-gothic-architecture.html.
“Gothic Architecture: an Introduction.” Khan Academy, Khan Academy, https://www.khanacademy.org/humanities/medieval-world/gothic1/a/gothic-architecture-an-introduction.
Leave a Reply