Lecture review:
Printing in China began and spread through Asia. Chop seals were in use as a replacement to the traditional handwritten signature and a status symbol of professionalism. The Diamond Sutra was created a 16-foot long scroll. In Europe, Churches obtained massive amounts of power politically and financially. Because of this majority of printed works were religious due to their high costs. This made Illuminated Manuscript and prayer books a status symbol worth similar to a farm. Parchment was the new innovation for books being bound into codices. Half uncials were developed by monks becoming a precursor to lower case.

An example of the Gutenberg Printing Press.
Gutenberg’s Printing Press.
Gutenberg worked as a goldsmith before venturing towards making a printing press. He used his training as a craftsman to help him create the design for the first iteration of the printing press. The press used type blocks that were movable to create strings of letters into words and sentences. With the addition of his new oil inks, he printed the Gutenberg Bible which was a 42 line bible that would become the first mass-produced text.

A living copy of the Gutenberg Bible.
Gutenberg practised his inventions with prototypes that have been long since lost. The final version allowed for colours to be added through several passes with different coloured ink being applied in succession. Also added was a new form style for type which allowed for several brass characters to be used as one block giving ease of use when being reused again and again.
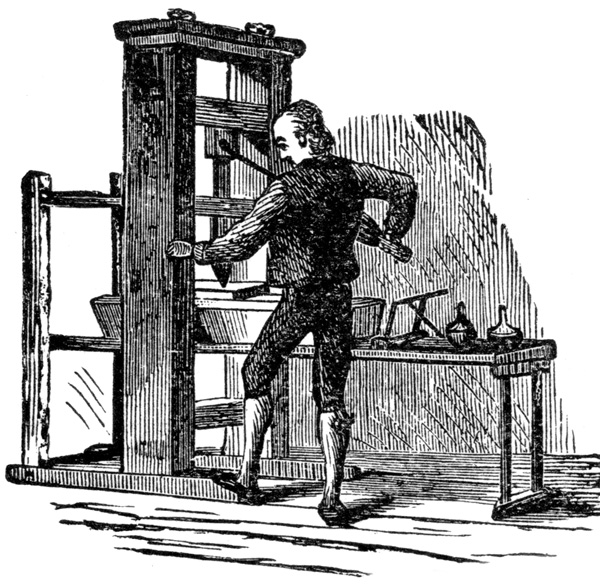
A wood print of the Gutenberg press with a press hand printing or cleaning.
Gutenberg was the first to make his types out of a lead, tin and antimony alloy, allowing for a softer metal that held shape and produced high-quality prints. Along with his innovative type he is believed to be the first to use a new oil-based ink being more durable and permanent then water-based inks that were being used.
Sources:
- https://www.britannica.com/technology/printing-press
- https://www.livescience.com/43639-who-invented-the-printing-press.html
- https://ozgeozva312.wordpress.com/2011/11/22/the-gutenberg-bible/
Leave a Reply