Jean-Michel Basquiat (December 22, 1960 – August 12, 1988) was an American artist who was known for his raw gestural style of painting with graffiti-like images and scrawled text.
Life
- Basquiat was born in Brooklyn, New York, on December 22, 1960. His mother, Matilde Basquiat, attached great importance to his artistic passion and enrolled him as a junior member of the Brooklyn Museum of Art.
- In 1967, Basquiat started attending Saint Ann’s School, an arts-oriented exclusive private school.
- In September 1968, at the age of seven, Basquiat underwent surgery to remove the spleen after being hit by a car, which led him to read the famous medical and art treatise “Gray’s Anatomy”. The sinewy bio-mechanical images of this text and those equally linear personages were believed having great influence in his mature, graffiti-inscribed canvases.
- The misfortune happened, constantly, Basquiat’s parents separated, and he and his sisters lived in Puerto Rico with their father from 1974 to 1976. His mother was diagnosed with mental illness and was eventually admitted to a shelter.
- Beauce of the broken family, Basquiat dropped out of Edward R. Murrow High School and left home at the age of 17.

- Basquiat lived on the street, with friends or in abandoned buildings, and has graffiti activities with graffiti artists Al Diaz and Shannon Dawson. They worked under the pseudonym SAMO, an acronym for “Same Old Shit”.
- On December 11, 1978, Basquiat and Diaz ended their friendship, The SAMO was ended with the epitaph “SAMO IS DEAD”, inscribed on the walls of SoHo buildings in 1979.
- In June 1980, Basquiat’s achievement raised into a new level because of his participation in The Times Square Show, a multi-artist exhibition sponsored by Collaborative Projects Incorporated (Colab) and Fashion Moda. which made him noticed by various critics and curators.

- In particular, the Italian gallerist Emilio Mazzoli saw the exhibition and invited Basquiat to Modena (Italy) to have his first world solo show, that opened on May 23, 1981.
- Furthermore, Basquait had a revolutionary advancement in 1982, not only his six solo shows in cities worldwide as the youngest artist ever to be included in Documenta but the creation of about 200 artworks and his signature black oracle figure.

- Unfortunately, the era background and social environment still made him a serious pressure, especially, as being a young black man artist. Basquiat later addicted to heroin and cocaine which were considered as a solution for those unsolvable problems.
- Although he attempted to get rid of the drug dependence, on August 12, 1988, he died of a heroin overdose at his art studio on Great Jones Street.
Style
Basquiat’s art career had at least twice breakthroughs. At the most beginning, his drawings were still like the seeds which contained a powerful spirit but did not really display his appearance. Those initial sketches were more like miniatures as a part of his future creation.
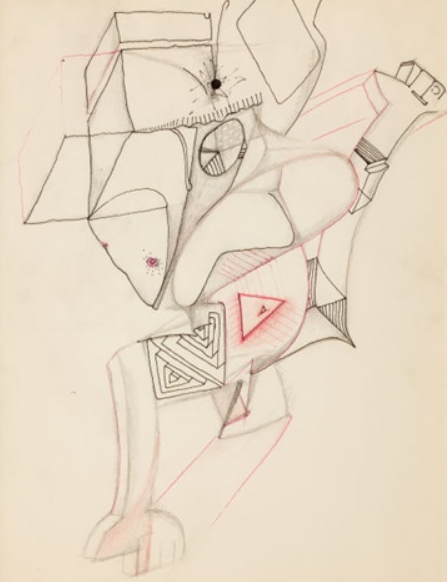
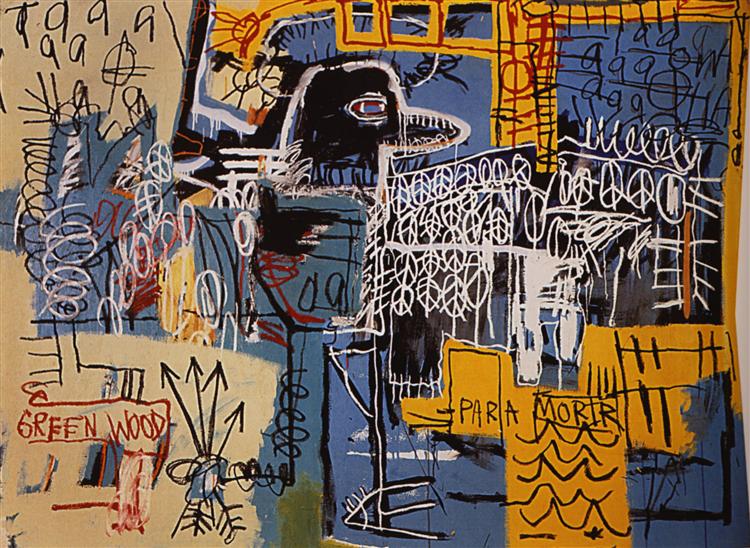
Furthermore, in 1982, Basquiat’s creation began to have a more obvious main theme, the black figure. Although the time period was not long, it is hard to say this element which appeared in hundreds of his works was not a constant development of Basquiat’s art cognition. Basquiat used this figure reflected a lot of social problems with the context in his paintings, and some of his self-portraits also used it as the basis. His arts are really hard to tell an exactly simple meaning, but really has the power of expressing the idea: “I am telling you”.

In his later works, the features of Neo-expressionism were further highlighted, which can obviously see his reaction against conceptual art and minimal art of the 1970s. He attempted to crazily increase the content in some of his work, and the using of colours became more contrastive and bright.
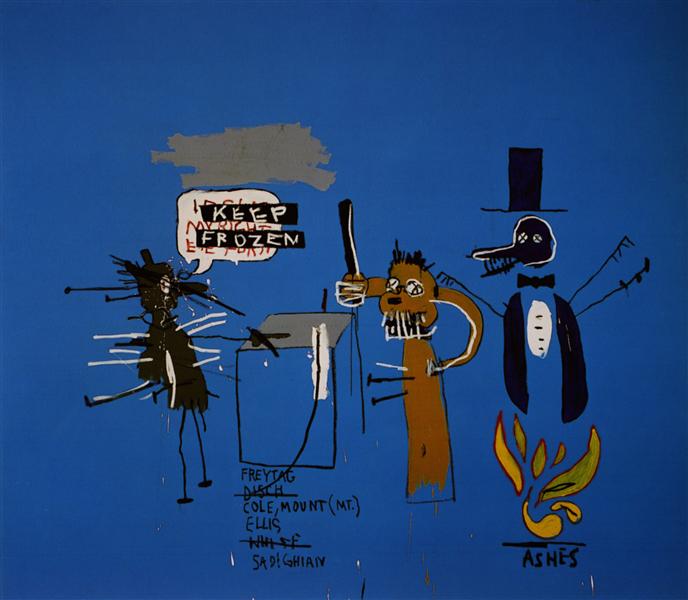


Personal Opinions
I really like the freedom in his arts. Because of the social background, Basquiat’s arts had talked about the topics of the races, politic and social class, and today’s critics still always connect his arts to those aspects, however, the innermost concept I see is what a passionate spirit who really in love with arts and freedom. Start in general, only the really enthusiasm can motive a person to crazily create the uncountable works in a short time. All his works even make me feel like created by an impulse which shortly motived his hands to do something without calm. However, his works are not something without thinking, they always have a direct topic and Basquiat just put his ideas on the audiences’ faces to let them see it by themselves. Indeed, I think this impulse is more important than the calmness because anyone will lose their impulses while the growing of age and the increasing of life experience. Basquiat was really lucky and brave in arts that he can express those innermost love so early

This passion was the energy of Basquiat’s art creation, but maybe also the source of his pressure in his later life. In his later creation, I can see his various attempts to the different types of arts, including further reflection on cubism, abstractionism, and expressionism.
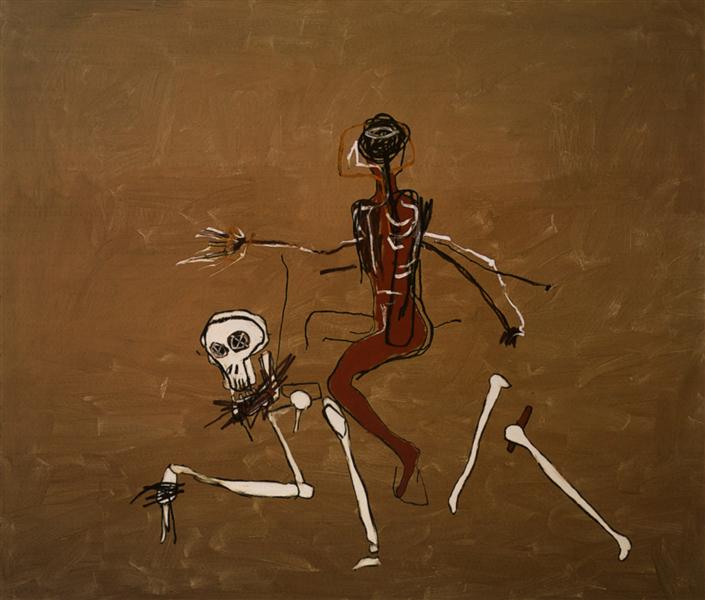



They are all really excellent works that obviously expressed Basquiat ‘s ideas and emotions. However, I think the sudden success and change of his life made him an extreme perfectionist who fears the failures and “not good enough”. This kind of mental pressure further developed by social attention and ultimately caused his tragedy of life.
References
https://www.wikiart.org/en/jean-michel-basquiat https://www.wikiart.org/en/jean-michel-basquiat/untitled-6 https://www.theartstory.org/artist/basquiat-jean-michel/life-and-legacy/ https://www.wikiart.org/en/jean-michel-basquiat/king-pleasure https://www.wikiart.org/en/jean-michel-basquiat/exu https://www.wikiart.org/en/jean-michel-basquiat/self-portrait-as-a-heel-part-two https://www.wikiart.org/en/jean-michel-basquiat/cabeza https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Jean-Michel_Basquiat https://www.britannica.com/biography/Jean-Michel-Basquiat https://www.wikiart.org/en/jean-michel-basquiat/rose-head



.jpg)
.jpg)



.jpg)